Difference between revisions of "Depth of syntactic constructions"
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
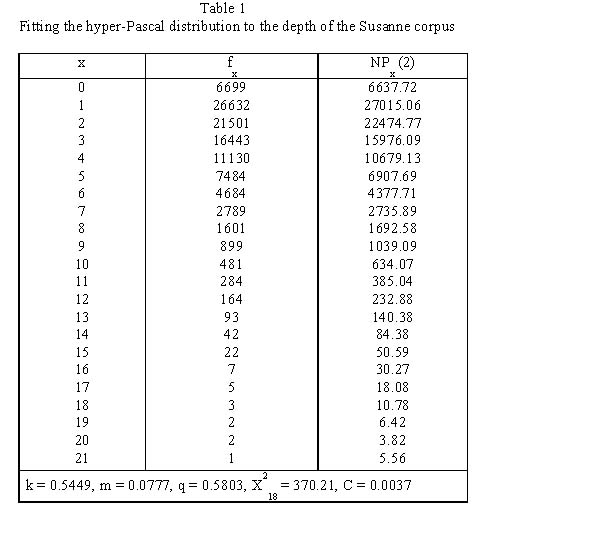
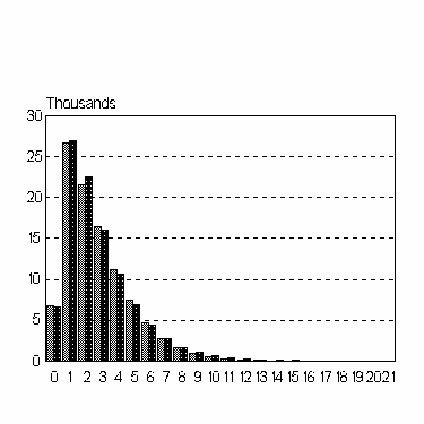
Köhler and Altmann (2000) considered the depth of embedding in the Susanne corpus and obtained the results presented in Table 1 and Fig. 1. | Köhler and Altmann (2000) considered the depth of embedding in the Susanne corpus and obtained the results presented in Table 1 and Fig. 1. | ||
| − | + | <div align="center">[[Image:Tabelle1_DoSC.jpg]]</div> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
<div align="center">[[Image:Grafik1_DoSC.jpg]]</div> | <div align="center">[[Image:Grafik1_DoSC.jpg]]</div> | ||
Latest revision as of 13:28, 27 June 2006
1. Problem and history
Depth (of embedding) of a syntactic construction is defined as the „number of steps from S to the given constituent, by applying production rules“ (Köhler, Altmann 2000). In practice, the sentence is analyzed in form of a graph-theoretical tree and the depth is the length of the way from S to the given symbol. The problem is to find the distribution of depth (x) in a text or in a corpus.
The first concept of depth was proposed by Yngve (1960, 1961). Different reserchers used it for typological purposes (Householder 1960; Papp 1966; Altmann, Lehfeldt 1973). It can be defined in the framework of any grammat. Köhler (1999) studied the dependence of depth on position (see Vol. 2); Köhler and Altmann (2000) derived the distribution of depth in a corpus.
2. Hypothesis
The depth of syntactic construction abides by the hyper-Pascal distribution.
3. Derivation
For the derivation the following quantities are necessary (Köhler, Altmann 2000) minT – the requirement of limiting the depth of embedding which represents the limitation of the language processing memory; maxH – the requirement of maximazing compactness. This enables us diminishing the complexity of the subordinated level of embedding by embedding constituents into the given level… minX on the level m corresponds to the requirement maxH on the level m+1; E – a variable representing the average degree of fullness, the default value of complexity.
Assumptions: Depth x is directly proportional to depth x-1, the proportionality being given by the default value of complexity E. The requirement maxH increases the tendency towards greater depth, minT restricts is. Thus we obtain
(1)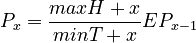 .
.
Setting maxH = k-1, minT = m-1, E = q and solving (1) results in the hyperpascal distribution
(2)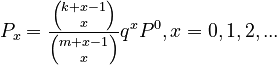
where 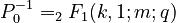 .
.
Example: The distribution of depth in the Susanne corpus
Köhler and Altmann (2000) considered the depth of embedding in the Susanne corpus and obtained the results presented in Table 1 and Fig. 1.
Since the sample size is very great (N = 101138), the usual chi-square test is inappropriate. Instead, one used the contingency coefficient 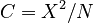 , which yields satisfactory results.
, which yields satisfactory results.
4. Authors: G. Altmann
5. References
Altmann, G., Lehfeldt,W. (1973). Allgemeine Sprachtypologie. München: Fink.
Householder, F.W.Jr. (1960). First thoughts on syntactic indices. International Journal of American Linguistics 26, 195-197.
Köhler, R. (1999). Syntactic structures: Properties and interrelations. J. of Quantitative Linguistics 6, 46-57.
Köhler, R., Altmann, G. (2000). Probability distributions of syntactic units and properties. J. of Quantitative Linguistics 7, 189-200.
Papp, F. (1966). On the depth of Hungarian sentences. Linguistics 25, 58-77.
Yngve, V. (1960). A model and a hypothesis for language structure. Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society 104, 444-446.
Yngve, V. (1961). The depth hypothesis. In: Jakobson, R. (ed.), Structure of Language and ist Mathematical Aspects: 130-138. Providence, R:I.: American Mathematical Society.