Difference between revisions of "Sound change"
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
The approach is based on Zipf´s ''Principle of least effort'' according to which the increasing production effort of a sound increases the probability of its change (Zipf 1935, 1949). | The approach is based on Zipf´s ''Principle of least effort'' according to which the increasing production effort of a sound increases the probability of its change (Zipf 1935, 1949). | ||
| − | Boretzky (1977: 119) says it explicitely: “Die Sprecher sind bestrebt, die Laute | + | Boretzky (1977: 119) says it explicitely: “Die Sprecher sind bestrebt, die Laute beizubehalten, zu deren Artikulation wenig Anstrengung erforderlich ist, und die Laute als erste zu verändern oder ganz wegfallen zu lassen, deren Hervorbringung besonders viel Energie erfordert.“ |
The first quantification goes back to Job (1983) who derived a formula for the probability of change depending on articulation effort. Since articulation effort is merely one side of Zipf´s principle, the effort of the hearer in perceiving and decoding the sound must be taken into account, too. The first extended model was derived by Job and Altmann (1985) whose further extension was performed by Prün (1995). | The first quantification goes back to Job (1983) who derived a formula for the probability of change depending on articulation effort. Since articulation effort is merely one side of Zipf´s principle, the effort of the hearer in perceiving and decoding the sound must be taken into account, too. The first extended model was derived by Job and Altmann (1985) whose further extension was performed by Prün (1995). | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
3.1. The “effort” model | 3.1. The “effort” model | ||
| − | Let A be the articulation effort of the speaker, <math>A \ | + | Let <math>A</math> be the articulation effort of the speaker, <math>A\in(0,M)</math>, then the perception effort of the hearer is its complement, i.e. <math>M - A</math>. Let further <math>A/M = x \in (0,1)</math> be the normed articulation effort and <math>w</math> the need for change. |
Then it holds for this need that | Then it holds for this need that | ||
| − | (1)<math> \frac{dw}{dx} = \frac{aw}{1-x} - \frac{bw}{x}</math> | + | (1) <math> \frac{dw}{dx} = \frac{aw}{1-x} - \frac{bw}{x}</math>. |
| − | One assumes that the greater x (= normed effort), the greater the need for change with the speaker (= aw) and the smaller with the hearer (= bw). | + | One assumes that the greater <math>x</math> (= normed effort), the greater the need for change with the speaker (= <math>aw</math>) and the smaller with the hearer (= <math>bw</math>). |
The solution of (1) yields | The solution of (1) yields | ||
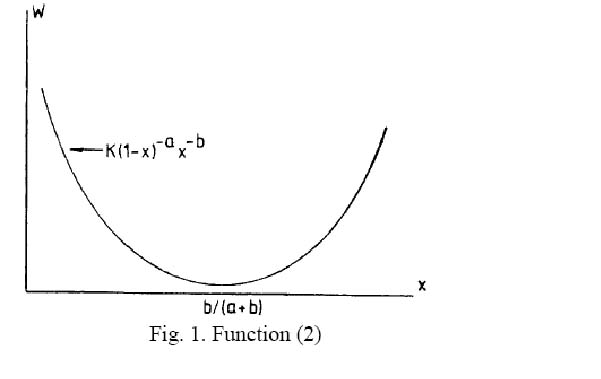
| − | (2)<math> w = K(1-x)^{-a}x^{-b}, \quad 0<x<1</math> | + | (2) <math> w = K(1-x)^{-a}x^{-b}, \quad 0<x<1</math>, |
presented graphically in Fig. 1. | presented graphically in Fig. 1. | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
| − | If we consider w as the probability of the need for change, then K is the norming constant which can be obtained as the usual beta function, i.e. we obtain finally the probability function | + | If we consider <math>w</math> as the probability of the need for change, then <math>K</math> is the norming constant which can be obtained as the usual beta function, i.e. we obtain finally the probability function |
| − | (3)<math> f_w(x) = \frac{1}{B(1-a, 1-b)}(1-x)^{-a}x^{-b}, \quad 0<x<1</math> | + | (3) <math> f_w(x) = \frac{1}{B(1-a, 1-b)}(1-x)^{-a}x^{-b}, \quad 0<x<1</math>. |
| − | The minimum of this curve is x = b/(a+b). | + | The minimum of this curve is <math>x = b/(a+b)</math>. |
| − | In order to estimate the probability of change, we use the distribution function of (3) and compute the probability of a change of a sound as | + | In order to estimate the probability of change, we use the distribution function of (3) and compute the probability of a change of a sound as follows. |
| − | (a)If the effort of the speaker is x > b/(a+b) then we compute | + | (a) If the effort of the speaker is <math>x > b/(a+b)</math>, then we compute |
| − | (4)<math> P_w(x) = \frac{1}{B(1-a, 1-b)}\int_{b/(a+b)}^{x}(1-x)^{-a}x^{-b}dx, \quad 0<x<1</math> | + | (4) <math> P_w(x) = \frac{1}{B(1-a, 1-b)}\int_{b/(a+b)}^{x}(1-x)^{-a}x^{-b}dx, \quad 0<x<1</math>, |
| − | i.e. the plane under the curve from its minimum to x. | + | i.e. the plane under the curve from its minimum to <math>x</math>. |
| − | (b) If the effort of the speaker is x < b/(a+b), then we compute | + | (b) If the effort of the speaker is <math>x < b/(a+b)</math>, then we compute |
| − | (5)<math> P_w(x) = \frac{1}{B(1-a, 1-b)}\int_x^{b/(a+b)}(1-x)^{-a}x^{-b}dx, \quad 0<x<1</math> | + | (5) <math> P_w(x) = \frac{1}{B(1-a, 1-b)}\int_x^{b/(a+b)}(1-x)^{-a}x^{-b}dx, \quad 0<x<1</math>. |
| − | No testing has been performed as yet and the parameters a and b have not been interpreted physically. | + | No testing has been performed as of yet and the parameters <math>a</math> and <math>b</math> have not been interpreted physically. |
'''3.2. Prün´s extension''' | '''3.2. Prün´s extension''' | ||
| − | Since in sense of Zipf a change depends also on the frequency of the sound, Prün (1995) | + | Since in the sense of Zipf a change depends also on the frequency of the sound, Prün (1995) extended the above formula inserting in it the relative frequency <math>f</math> of the sound and obtained |
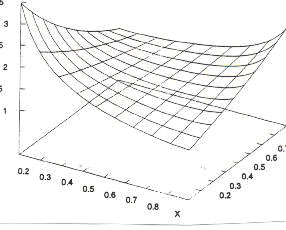
| − | (6)<math> | + | (6) <math> y = K(1-x)^{-af}\cdot x^{-b(1-f)}</math>. |
The differential equation leading to this result is | The differential equation leading to this result is | ||
| − | (7)<math> \left( \frac{dy}{dx} + \frac{dy}{df}\right)\frac{1}{y} = af - b (1-f)+b \ln x - a \ln (1-x)</math> | + | (7) <math> \left( \frac{dy}{dx} + \frac{dy}{df}\right)\frac{1}{y} = af - b (1-f)+b \ln x - a \ln (1-x)</math>, |
| − | but it | + | but it has not been interpreted yet. A graphical example can be seen in Fig. 2. |
<div align="center">[[Image:Grafik2_SC.jpg]]</div> | <div align="center">[[Image:Grafik2_SC.jpg]]</div> | ||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
| − | '''4. Authors: G. Altmann | + | '''4. Authors''': U. Strauss, G. Altmann |
'''5. References''' | '''5. References''' | ||
Latest revision as of 11:42, 10 June 2009
1. Problem and history
The approach is based on Zipf´s Principle of least effort according to which the increasing production effort of a sound increases the probability of its change (Zipf 1935, 1949). Boretzky (1977: 119) says it explicitely: “Die Sprecher sind bestrebt, die Laute beizubehalten, zu deren Artikulation wenig Anstrengung erforderlich ist, und die Laute als erste zu verändern oder ganz wegfallen zu lassen, deren Hervorbringung besonders viel Energie erfordert.“ The first quantification goes back to Job (1983) who derived a formula for the probability of change depending on articulation effort. Since articulation effort is merely one side of Zipf´s principle, the effort of the hearer in perceiving and decoding the sound must be taken into account, too. The first extended model was derived by Job and Altmann (1985) whose further extension was performed by Prün (1995).
2. Hypothesis
The probability of change of a sound is a function of its articulation and perception effort. (Job, Altmann 1985)
“Articulation effort” is the energy necessary to utter the sound. It can be measured e.g. by muscle participation in articulation. “Perception effort” could be measured as a function of the proportion of confusions of the given sound with other sounds (cf. Benzecri 1970; Clarke 1957; Conrad 1963; Conrad, Hull 1964; Gersic, Naumann, Altmann 1985; Klatt 1968; Miller, Nicely 1976; Nakatani 1972; Singh 1966, 1971; Thürmann 1974; Tversky 1977; Wickelgren 1965a,b,c, 1966a,b,c; Wilson 1963).
3. Derivation
3.1. The “effort” model
Let 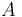 be the articulation effort of the speaker,
be the articulation effort of the speaker, 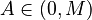 , then the perception effort of the hearer is its complement, i.e.
, then the perception effort of the hearer is its complement, i.e. 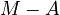 . Let further
. Let further 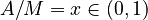 be the normed articulation effort and
be the normed articulation effort and 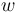 the need for change.
Then it holds for this need that
the need for change.
Then it holds for this need that
(1) 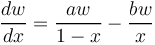 .
.
One assumes that the greater 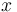 (= normed effort), the greater the need for change with the speaker (=
(= normed effort), the greater the need for change with the speaker (= 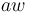 ) and the smaller with the hearer (=
) and the smaller with the hearer (= 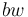 ).
The solution of (1) yields
).
The solution of (1) yields
(2) 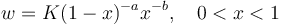 ,
,
presented graphically in Fig. 1.
If we consider 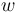 as the probability of the need for change, then
as the probability of the need for change, then 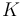 is the norming constant which can be obtained as the usual beta function, i.e. we obtain finally the probability function
is the norming constant which can be obtained as the usual beta function, i.e. we obtain finally the probability function
(3) 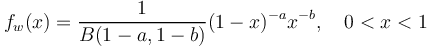 .
.
The minimum of this curve is 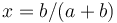 .
In order to estimate the probability of change, we use the distribution function of (3) and compute the probability of a change of a sound as follows.
.
In order to estimate the probability of change, we use the distribution function of (3) and compute the probability of a change of a sound as follows.
(a) If the effort of the speaker is 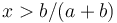 , then we compute
, then we compute
(4) 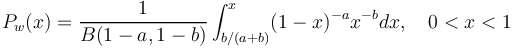 ,
,
i.e. the plane under the curve from its minimum to 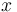 .
.
(b) If the effort of the speaker is 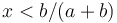 , then we compute
, then we compute
(5) 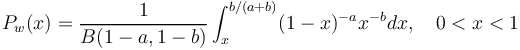 .
.
No testing has been performed as of yet and the parameters 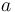 and
and 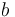 have not been interpreted physically.
have not been interpreted physically.
3.2. Prün´s extension
Since in the sense of Zipf a change depends also on the frequency of the sound, Prün (1995) extended the above formula inserting in it the relative frequency 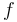 of the sound and obtained
of the sound and obtained
(6) 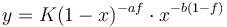 .
.
The differential equation leading to this result is
(7) 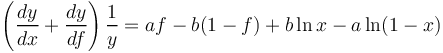 ,
,
but it has not been interpreted yet. A graphical example can be seen in Fig. 2.
4. Authors: U. Strauss, G. Altmann
5. References
Job, U. (1983). Bemerkungen zu einer theoreti¬schen Konzeption von Sprachwandel. In: K.-H. Best und J. Kohlhase (eds.), Exakte Sprachwandelforschung: 5 – 19. Göttingen: Edition Herodot.
Job, U., Altmann, G. (1985). Ein Modell der anstrengungsbedingten Lautveränderung. Folia Linguistica Historica 6, 401-407.
Lehfeldt, W. (2005). The fall of jers in the light of Menzerath´s law. In Grzybek, P. (ed.), Word length studies and related issues: 215-218. Boston/Dordrecht: Kluwer.
Lehfeldt, W., Altmann, G. (2000). Padenie reducirovannych v svete zakona P. Mencerata. Russian Linguistics 26, 327-344.
Lehfeldt, W., Altmann, G. (2003). The process of the fall of the reduced vowels in Old Russian in the light of the Piotrovskii law. Russian Lingusitics 27, 141-149.
Prün, C. (1995). Die linguistischen Hypothesen von G.K. Zipf aus systemtheoretischer Sicht. Trier: Magisterarbeit.